

We’re not talking about the “Sit. Shake.” kind of shake. Nor the fun way they shake off water starting from their nose all the way to the end of their tail. (FYI, dogs can shake off 70% of the water on their fur in just four seconds!)
No, we’re talking about that full-body trembling you’ve likely seen your pooch do from time to time. Why do they do it? And is it something you should be worried about? Let’s shake a leg and find out.
A majority of dog owners in an IAMS™ survey* (64%) think dogs shake because they’re cold. Other top responses were because they’re scared (57%) or anxious (54%).
High-fives all around because it turns out there are a number of reasons dogs shake, and all those are possible correct answers.

Just like their owners, dogs will often shiver when cold.
Opens a new windowDr. Tammie King, Applied Behavior Technical Leader at Waltham Petcare Science Institute, says: “Dogs shiver in response to falling temperatures. Dogs with short or no hair are especially susceptible. You should get them warm, put coats on them or bring them inside.” Same goes for you.
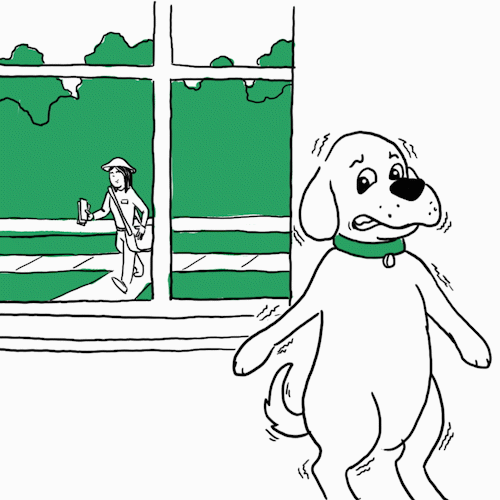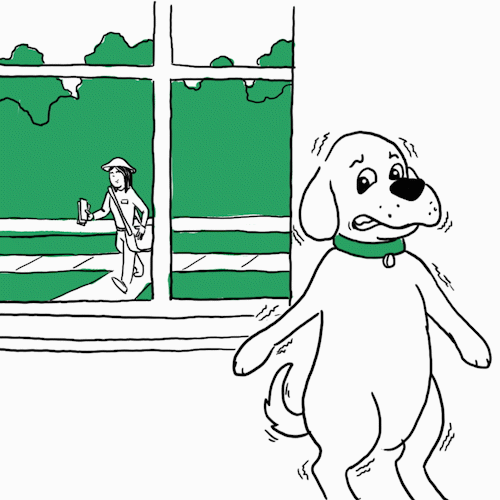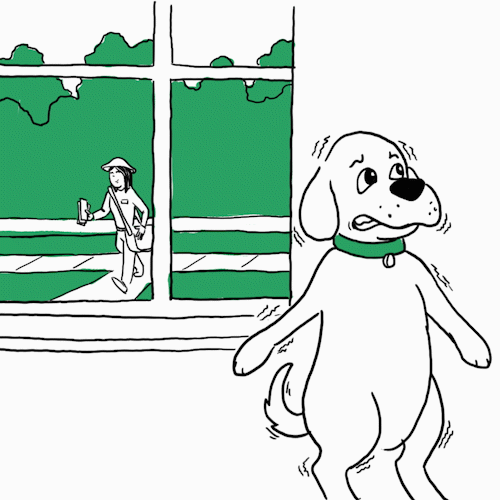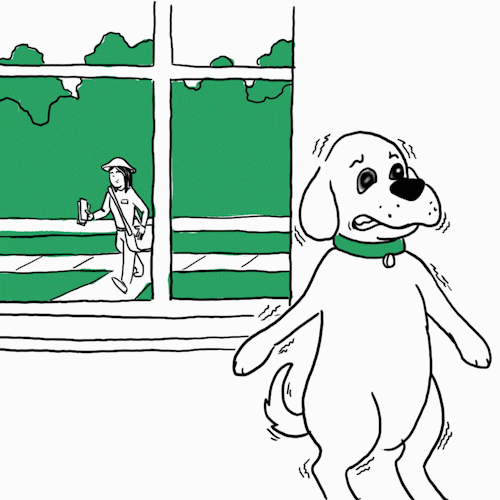
“Shaking is a response to epinephrine or adrenaline secretion — a sign of anxiety where the dog is on high alert,” says
Opens a new windowJames Serpell, B.S., Ph.D., Professor of Humane Ethics & Animal Welfare at the University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine. You may notice this when you’re at the vet or there’s a situation where they feel threatened. Dr. Serpell also offers a way to help in some cases: “Identify what’s triggering the behavior. Provide them comfort. Going forward, you can gradually desensitize your pet to the thing it’s afraid of.” Unless it’s clowns. Those are always scary.
Trembling can also be a sign of serious issues like injury, poisoning or kidney disease. Opens a new windowDr. Jo Gale, BVetMed CertLAS MRCVS, Senior Manager, Global Science Advocacy at Waltham Petcare Science Institute urges pet owners to be vigilant: “If a pet is unwell in another way, they could be trembling.” If their shaking is accompanied by symptoms like diarrhea, limping or vomiting, you should consult your vet straight away.
*Surveyed U.S. dog owners, age 18+
Sample Size: n=201
Fielded May 8-10, 2020


Bloat is a life-threatening condition that acts rapidly and can lead to death within hours if not recognized and treated immediately. Unfortunately, the cause of bloat remains unknown at this time.
The scientific term for bloat is gastric dilatation-volvulus or GDV. Bloat is characterized by rapid and abnormal expansion of the stomach with gas (dilatation). This can be followed by rotation of the stomach (volvulus). This rotation closes both the entry to and exit from the stomach. The blood vessels also are closed down, and blood flow is restricted.
What follows is an increase in pressure inside the stomach and compression of the surrounding organs. Eventually, shock will occur as a result of the restricted blood flow. Here are a few key facts about bloat:
Bloat is a true medical emergency, and early identification and treatment is critical to survival.
In the early stages of bloat, the dog will be very uncomfortable. You might see him pacing and whining or trying unsuccessfully to get into a comfortable position. He might seem anxious, might lick or keep staring at his stomach, and might attempt to vomit, without success.
Other indications of bloat can include weakness, swelling of the abdomen, and even signs of shock. Signs of shock are increased heart rate and abnormally rapid breathing.
If you notice these signs, call your veterinarian immediately!
These suggestions could help you prevent bloat in your dog. However, they are based on suspected risk factors and are not guaranteed to prevent the onset of bloat.
Another way you might help prevent bloat is to feed a high-quality, highly digestible food with normal fiber levels.
Feeding management offers the best method available for reducing risk until the exact cause of bloat can be identified. Although not 100% effective, these measures can reduce the number of dogs that face this serious, life-threatening condition.