

We’re not talking about the “Sit. Shake.” kind of shake. Nor the fun way they shake off water starting from their nose all the way to the end of their tail. (FYI, dogs can shake off 70% of the water on their fur in just four seconds!)
No, we’re talking about that full-body trembling you’ve likely seen your pooch do from time to time. Why do they do it? And is it something you should be worried about? Let’s shake a leg and find out.
A majority of dog owners in an IAMS™ survey* (64%) think dogs shake because they’re cold. Other top responses were because they’re scared (57%) or anxious (54%).
High-fives all around because it turns out there are a number of reasons dogs shake, and all those are possible correct answers.

Just like their owners, dogs will often shiver when cold.
Opens a new windowDr. Tammie King, Applied Behavior Technical Leader at Waltham Petcare Science Institute, says: “Dogs shiver in response to falling temperatures. Dogs with short or no hair are especially susceptible. You should get them warm, put coats on them or bring them inside.” Same goes for you.
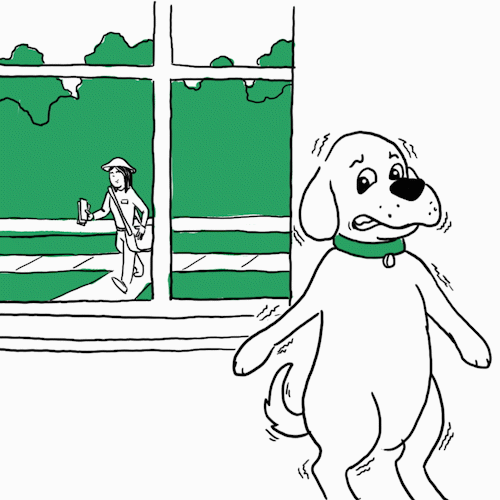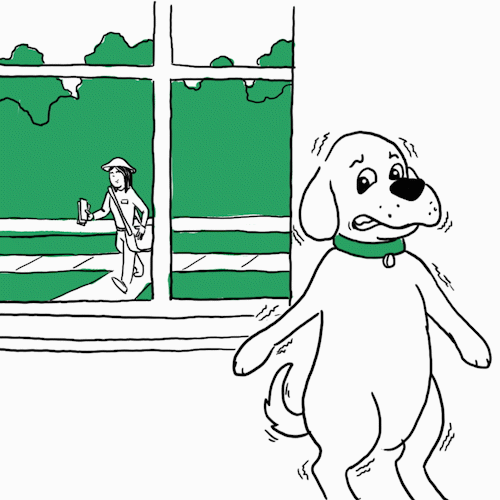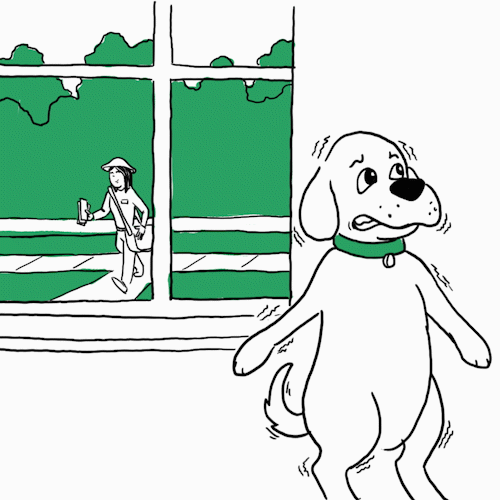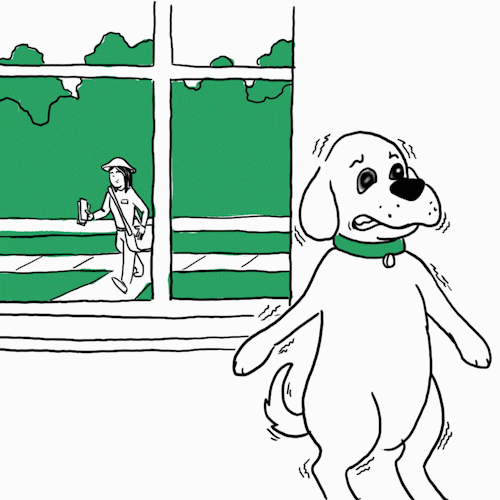
“Shaking is a response to epinephrine or adrenaline secretion — a sign of anxiety where the dog is on high alert,” says
Opens a new windowJames Serpell, B.S., Ph.D., Professor of Humane Ethics & Animal Welfare at the University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine. You may notice this when you’re at the vet or there’s a situation where they feel threatened. Dr. Serpell also offers a way to help in some cases: “Identify what’s triggering the behavior. Provide them comfort. Going forward, you can gradually desensitize your pet to the thing it’s afraid of.” Unless it’s clowns. Those are always scary.
Trembling can also be a sign of serious issues like injury, poisoning or kidney disease. Opens a new windowDr. Jo Gale, BVetMed CertLAS MRCVS, Senior Manager, Global Science Advocacy at Waltham Petcare Science Institute urges pet owners to be vigilant: “If a pet is unwell in another way, they could be trembling.” If their shaking is accompanied by symptoms like diarrhea, limping or vomiting, you should consult your vet straight away.
*Surveyed U.S. dog owners, age 18+
Sample Size: n=201
Fielded May 8-10, 2020


Nutrients like protein, fat, vitamins and minerals are vital to the skin and coat health of dogs. Your dog’s coat is made up almost entirely of protein. If his diet doesn’t contain enough protein quantity and quality, hair might fall out or become dry, weak and brittle. Likewise, his skin is made up of tightly packed flat cells with tough membranes made of proteins and fats. Without proper amounts of these nutrients, the cell membranes weaken, allowing water to escape and bacteria and viruses to enter more easily.
Make sure your dog is getting the following nutrients to keep his coat and skin healthy.
Proteins are found in both animal-based and plant-based ingredients. However, animal-based proteins contain all the essential amino acids dogs need, whereas plant-based proteins might not contain enough of some essential amino acids.
Fats also are found in both animal- and plant-based ingredients and are incorporated into skin cells as fatty acids. In particular, linoleic acid is essential for a dog’s skin and coat health. Without enough linoleic acid, dogs might experience a dull and dry coat, hair loss, greasy skin and increased susceptibility to skin inflammation.
Linoleic acid is found in chicken fat and vegetable oils (such as corn and soybean). IAMS™ research has also found that the fatty acids in vitamin-rich fish oils help promote excellent skin and coat health.
Your dog needs vitamins and minerals for a healthy skin and coat. The best way to provide these nutrients is by feeding a complete and balanced diet full of essential vitamins and minerals, rather than giving him supplements.
Vitamin or Mineral Importance to Skin and Coat Health
Vitamin A Necessary for growth and repair of skin
Vitamin E Protects skin cells from oxidant damage
Vitamin C Helps heal wounds
Biotin Aids in the utilization of protein
Riboflavin (B2) Necessary for fat and protein metabolism
Zinc Necessary for fat and protein metabolism
Copper Involved in tissue, pigment, and protein synthesis
Diet can be a factor when changes in skin and coat condition occur, but the most common causes are season and life stage. As cold weather approaches, most dogs grow a thick coat to help keep heat in and cold air out. As the weather warms up, they shed their thick, heavy coat.
Most puppies are born with soft, fuzzy hair, but as they age, a coarser coat grows. Pregnant or nursing dogs also might experience a change in coat condition or hair loss. And, as with humans, a dog’s hair might thin out and become coarser and white as he reaches his mature years.