

Panting is when dogs breathe rapidly with their mouth open and tongue hanging out like a slobbery yo-yo. You know what we’re talking about. So other than as an effective method of drool distribution, why do they do it?
Some dogs may occasionally pant when they’re excited or afraid, but the main reason is to help keep themselves from overheating.
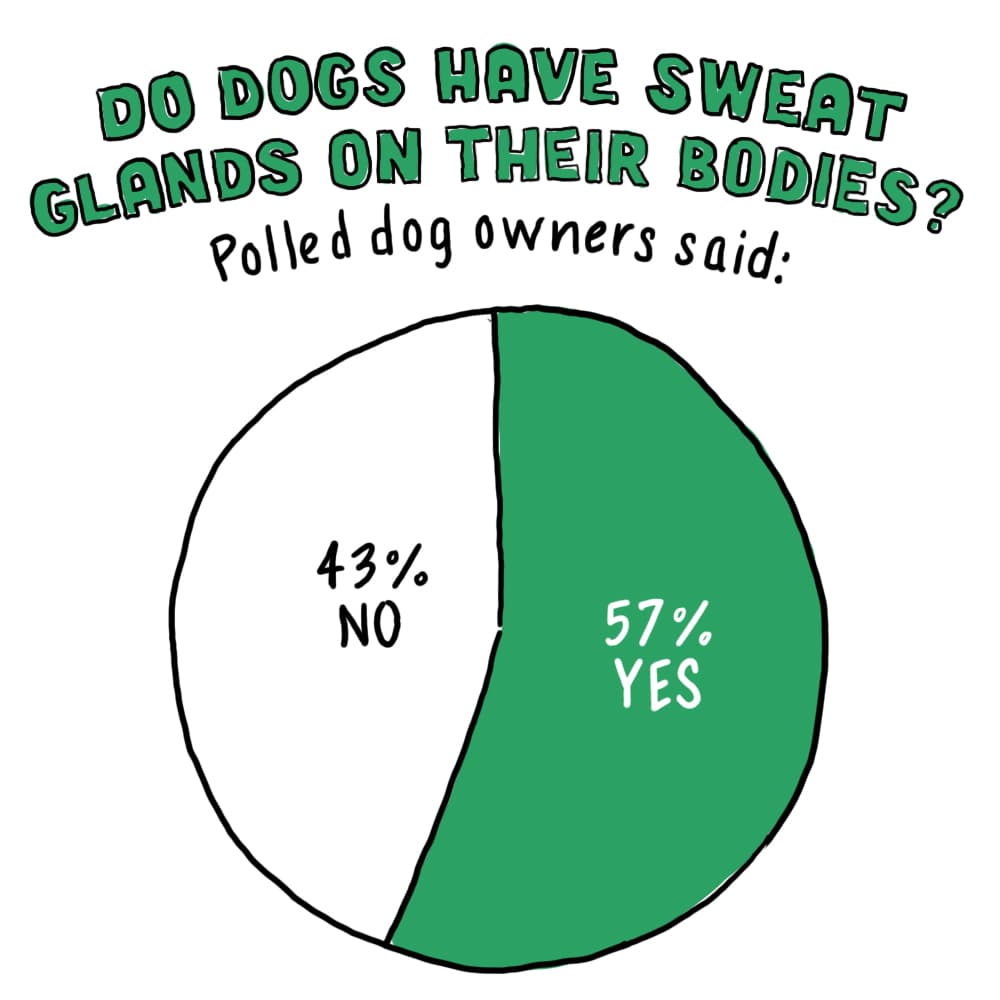
In a recent IAMS™ survey,* a majority of dog parents believed that dogs have sweat glands. But dogs don’t sweat like humans do. “We have glands all over our body. Dogs can’t do that,” says Opens a new windowDr. Jo Gale, BVetMed CertLAS MRCVS, Senior Manager, Global Science Advocacy at Waltham Petcare Science Institute. “They have sweat glands on their paw pads, but that’s the only place.” They rely on panting to let out warm air and bring in cooler air. All that drool and fluid in their mouth helps dissipate the heat as well. It’s like a big soggy air conditioner.
Most mammals, and even many birds, pant to regulate their temperatures. Humans are some of the only creatures who cool down by perspiration. Imagine what dogs think of us losing fluid from all over our bodies, sweating through our clothes and needing to wipe our faces all the time. Fortunately, they love us anyway.
Panting is normal, but it expends lots of water, so make sure Fido’s bowl is full of clean, cool H2O, especially during warmer months.
Opens a new windowDr. Tammie King, Applied Behavior Technical Leader at Waltham Petcare Science Institute, suggests “seeking out cool shade, giving them water and stopping physical activity.”
And it goes without saying — but we’re going to say it anyway — that you should never leave your dog in your vehicle on hot days. Even if they’re driving. Which you shouldn’t let them do either.
Some dogs run a higher risk of overheating. “It’s very easy for dogs to overheat on very hot days,” cautions Dr. Jo Gale. “Any dog with a squashed face — bulldogs, pugs, Pekingese — their nasal passages are not able to cool the air as much.” She added that dogs with heavy coats, overweight dogs, and very old or very young pets also can’t control their body temperature as effectively.
If your pooch seems to be panting more than usual or at unusual times, check to see if they’re having trouble breathing, are shaking, or their gums or tongue have noticeably changed color. If so, make sure they have access to water, get them to a cool place and contact your vet.
*Surveyed U.S. dog owners, age 18+
Sample Size: n=201
Fielded May 8-10, 2020


Pregnancy and nursing are not only responsible for many changes in a dog's body, but for changes in her lifestyle as well. If your dog is pregnant or nursing, pay special attention to her changing nutritional needs as she carries, delivers and nurses her puppies.
If you're planning to breed your female dog, it’s important to assess her body condition well in advance of breeding. Because of the physical demands of pregnancy and nursing, a dog with less-than-ideal health can experience problems:
Be sure to feed the proper amounts of a complete and balanced diet. This will support the mother's healthy weight and body condition before breeding and help maintain her health and that of her babies throughout pregnancy and lactation.
The gestation period for dogs is nine weeks. Pregnant dogs gain weight only slightly until about the sixth week, and then gain weight rapidly.
The energy requirements of pregnant dogs are reflected in the pattern of weight gain. Pregnant dogs will need to consume 25% to 50% more than their normal food intake by the end of pregnancy, but energy requirements do not increase until about the sixth week.
The best diet for pregnant and nursing dogs is a high-quality, nutrient-dense pet food formulated for all life stages or for growth. Although puppy diets are generally recommended for pregnant or nursing dogs, large-breed puppy formulas may not be appropriate for this use due to their adjusted energy and mineral content.
Pregnant dogs lose weight after giving birth, but their nutritional needs increase dramatically. Depending on litter size, nursing dogs might need two to three times their normal food requirement to nourish their pups. Be sure your nursing mom has plenty of water so she can generate the milk volume she needs to feed the litter.
To help your nursing dog get enough nutrition, you can try several tactics:
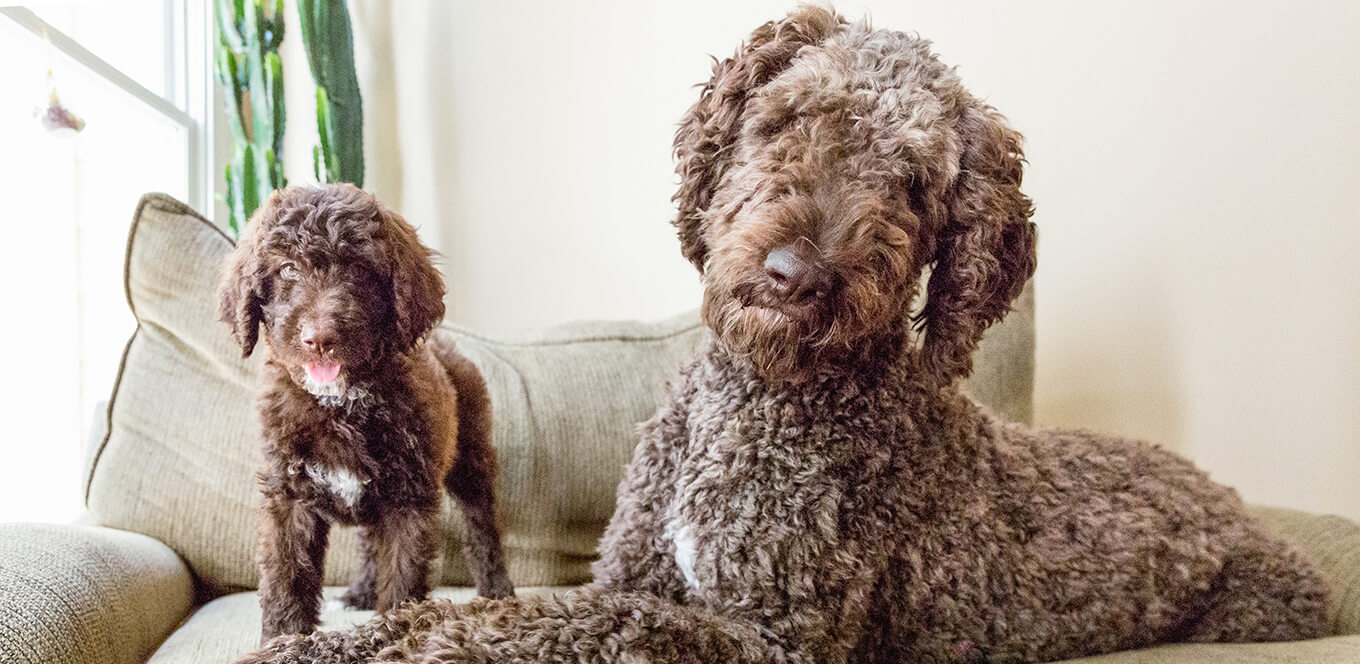

By four to five weeks after birth, most puppies are showing an interest in their mother’s food. Gradually, the puppies will begin eating more solid food and nursing less. At the same time, the nursing mother will usually begin eating less. Most puppies are completely weaned around age 7 to 8 weeks. By this time, the mother's energy requirement is back to normal, and she should be eating her normal pre-pregnancy diet.