

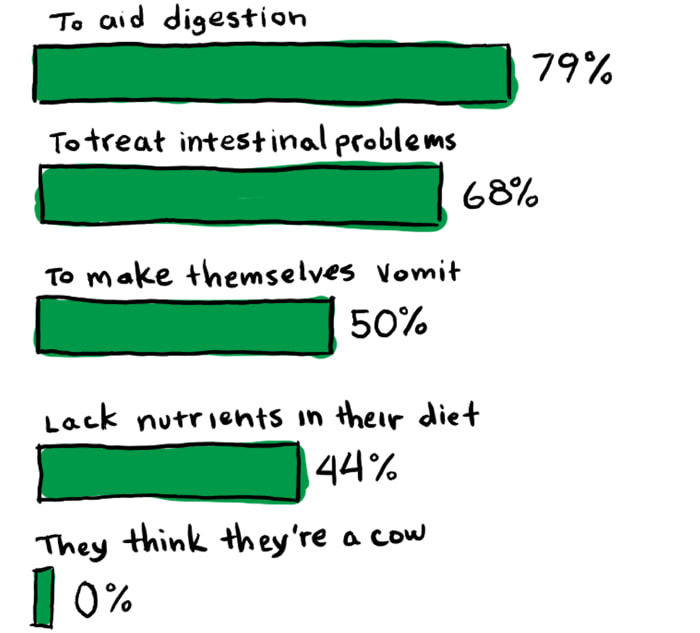
In a recent IAMS poll of dog owners,* 69% said their dog eats grass. That’s quite a lot. Owners also have quite a lot of theories on why their dog is noshing on the lawn.
It’s not just modern-day canines that eat grass. It’s likely something that has been going on for thousands of dog years. According to
Opens a new windowDr. Tammie King, Applied Behavior Technical Leader at Waltham Petcare Science Institute, “It is actually normal canine behavior. It has to do with innate behavior from canine ancestors. Potentially a remnant behavior.”
Dr. King also shared this with us: “A lot of people think dogs eat grass when they’re feeling ill, but studies have shown that’s not necessarily true.”
But then why do dogs eat grass? To get to the (grass)root of this issue, we asked
Opens a new windowDr. Jo Gale, BVetMed CertLAS MRCVS Senior Manager of Global Science Advocacy at Waltham Petcare Science Institute.
'There's no one reason. They just like the taste, texture and feel of the grass.'
So it’s perfectly fine if your pooch decides to have an occasional grass snack. Who doesn’t crave a salad every now and then?
However …
If your dog is getting adequate nutrition, there’s no need to worry. But the experts we talked with asked dog owners to please keep in mind the following:
· Grass that’s been treated with weed killer or pesticides should be off the menu.
· If your dog is eating grass excessively or routinely vomiting from eating grass, consult your vet.

Looking for the perfect dog food to pair with their side of sod slaw? IAMS has the answer for that, too.
*Surveyed U.S. dog owners, age 18+
Sample Size: n=201
Fielded May 8 to May 10, 2020


Is your dog really a finicky eater, or could it be something else? There are many factors to consider when you notice that your dog doesn't seem to be eating as usual.
If you're suspicious, take a closer look at exactly what he's eating each day. Does he get the occasional dog treat, or is someone sneaking him extra table scraps?
When you feed your dog a balanced, highly nutritious diet, nothing else is needed. In fact, extra treats can drastically alter your dog's normal intake of dog food. It's similar to the feeling you get after eating too much candy or potato chips. Are you interested in a full meal? Neither is your dog.
IAMS™ dog foods are nutritionally balanced and specifically formulated to meet the needs of dogs in all life stages, and with different lifestyles. There are dry, canned, and pouch varieties, plus options for senior or overweight pets, puppies, and dogs with reduced activity levels. Talk to your veterinarian or an IAMS Pet Care and Nutrition Center professional for advice on what's best for your dog.
Recommended feeding amounts are shown on every package. The guidelines are general suggestions for the amount of food you should feed your dog. Every dog is different and does not need the same amount of food. Your dog's activity level and his metabolic makeup are the determining factors. Start with the amount given in the feeding guidelines. Then, add or subtract food as you observe your dog's eating habits and weight.
Portion-Controlled Feeding: Divide the daily amount and feed at specific intervals. It is important to take away all leftover food after 15 to 20 minutes. This sets a pattern for your dog to follow. The portion-controlled feeding method is recommended for giant and large breeds as well as for overweight dogs. Portion control also works well for dogs with special needs.
Free-Choice Feeding: Feed the daily amount and let your dog eat at leisure. This method is recommended for use only with dry foods. Remember, dogs eat to meet their energy requirements. They quickly define their own daily portions when eating free-choice.
Water: Regardless of which food you choose to feed, your dog must have plenty of fresh, clean water. A good dog feeding tip is to place the water 3 to 5 feet from the food. This will help prevent your dog from gulping water and air in addition to food.
Routine: Dogs need it. Feeding at the same time and place every day establishes a comfortable eating pattern.
The Veterinarian: Regular visits help keep your dog happy and healthy!