

For most pet parents, the expense, time, and expertise involved in breeding dogs responsibly is beyond their reach. Here are some advantages to having your puppy spayed or neutered:
When to Spay or Neuter
Dogs should be spayed or neutered by the time they are 6 months old to avoid many dog health issues. Both operations are performed under anesthesia and may require an overnight stay at the veterinarian's office. Recovery time is quick, with most dogs resuming normal activity in a few days. Spaying (for females) consists of an ovario-hysterectomy.
Neutering involves the removal of the testicles. When you bring your puppy to the veterinarian's office for his first thorough examination, have the doctor explain the operation in detail and set up a time to have the procedure done.


Feeding your dog the right nutrients and a complete, balanced diet doesn’t have tobe a head-scratcher. Find out how to choose the right dog food, how often to feedyour dog, how to handle treats and supplements, and much more.
Jump to questions about:
So you’ve found a new cat you can’t wait to bring home to your growing fur family.While it may be tempting to simply put all cats in a room and let them work out the introductions, this can cause a lot of stress for new and resident cats alike. Here area few ways to help the introduction go smoothly.
How Do I Decide Which Food to Feed?
When deciding which pet food is right for your pet, consider these three factors:your dog’s life stage, lifestyle and overall condition. Life stage refers to whether your dog is a puppy, an adult or a senior. Lifestyle refers to how active or inactive your dog is normally. Condition refers to your dog’s overall health and body weight.
How Often Should I Feed My Dog?
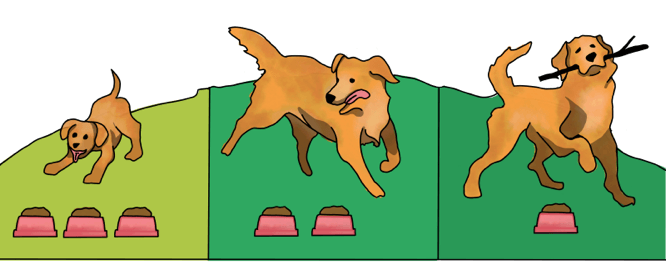
Puppies should be fed three times a day from weaning (3 to 6 weeks) to 4 months of age. After 4 months, they should be fed twice a day. Most dogs should continue to be fed twice a day throughout their life, although some pets do well with one feeding.
How Much Should I Give My Dog to Eat?
The amount to feed your dog depends on their age, size and activity level. Feeding guidelines, which list the daily-recommended portion, are included on all IAMS™packages. Start feeding with this amount and adjust according to your pet’s needs.Remember to divide the portion accordingly if you feed more than once a day.
When Should I Switch My Puppy to Adult Dog Food?
You should switch your puppy to a premium adult dog food like IAMS™ Lamb and Rice Recipe when they reach adult height. Small breeds that weigh less than 20pounds can usually start eating adult food between 9 and 12 months of age. Medium breeds weighing between 20 and 50 pounds can eat adult food at 12 to 14months of age. Large and giant breeds that weigh 50 or more pounds can transition from puppy food to adult dog food between 12 to 24 months of age. If you’re notsure, consult your vet.
What Is The Best Way to Introduce a New Diet to My Dog?
When changing your dog’s diet, it’s important to slowly introduce new food. Start by offering your dog’s daily portion in a ratio of 25% new food to 75% current food. During the next three days, gradually increase the amount of new food anddecrease the amount of the old food.
Should I Feed My Dog Both Wet and Dry Food?
Wet food is an excellent treat that can be fed alone or mixed with dry food. Although IAMS™ wet dog foods are nutritionally complete and balanced, you don’t have to offer wet food at every feeding. IAMS™ dry dog foods are formulated with high-quality protein sources such as such as chicken or lamb, and contain all the essential nutrients pets need. The crunchy texture of dry food also promotes healthy teeth and gums, and aids in overall good oral hygiene. In addition, some ofour dry dog foods contain a dental ingredient, sodium hexametaphosphate (HMP),to help block tartar build up on teeth during and after meals.

What Should I Feed My Dog If They’re Overweight?
If your dog is considered overweight for their breed and size, feeding a weight control dog food like IAMS™ Adult Healthy Weight, along with increasing their exercise and movement, can help address the issue. Don’t simply feed your dog less food — they still need to consume adequate protein, essential fatty acids and other nutrients even while they’re losing weight. And make sure to consult your vet before putting your dog on a weight management program.
What Should I Feed My Pregnant or Nursing Dog?
If your dog is pregnant or nursing, her nutritional needs have changed. The best food for a pregnant dog is a high-quality, nutrient-dense pet food formulated for all life stages, or for growth. A pregnant dog needs to consumer 25% to 50% more food than normal by the end of her pregnancy. A nursing dog should be fed a nutrient-dense diet such as IAMS™ Puppy and needs to eat two to three times her normal food requirement so she can nourish her puppies.
Why Does My Dog Need to Eat Protein?
Protein is an essential nutrient for dogs: It gives dogs amino acids that support healthy skin and a healthy coat, as well as muscles, tendons, ligaments and cartilage. High-quality animal-based proteins, like those found in chicken, lamb, fish and beef, contain all of the essential amino acids that dogs need to achieve optimal health.
How Can I Learn More about Pet Nutrition?
Contact MARS Petcare toll-free at 1-800-675-3849.
Will My Dog Be Bored Eating the Same Food All the Time?
No. Boredom with food is a human trait. Dogs are creatures of habit and usually are happy with just one food. Dogs generally eat to meet their energy or nutritional needs. They have very short digestive systems, and if their diet is abruptly or constantly changed, digestive disturbances can occur. Also, constant changes can make your dog a finicky eater.
Is It OK to Moisten Dry Food?
Adding water will not change the nutritional value of a dry pet food. However, once moisture is added, make sure your dog eats it relatively soon — and also discard any uneaten portion to avoid spoilage. Feeding dry food is usually encouraged because of the benefit to your dog’s dental health.
Will It Hurt My Dog If They Eat My Cat’s Food?
Cats and dogs have different nutritional requirements and should not eat each other’s food. For example, cats require a much higher level of taurine in their diet. An occasional venture into each other’s bowls will not be harmful, but is not recommended on a regular basis.
Can I Supplement Your Dog Foods with Vitamins, Minerals,Oils, etc.?
Our foods are nutritionally complete and balanced. Adding vitamins, minerals or oils can offset the balance the food provides. One of the benefits of feeding a high quality product is that it has been carefully balanced in proper ratios to provide optimal nutrition — nothing needs to be added.