A: My personal preference is not to use food at all. When I have trained dogs for obedience, I have always used the verbal praise-reward method. It works well, especially with some dogs who are not motivated by food rewards.
Many people do use treat-based training with success, but I don't recommend offering table scraps as the treat. Giving a dog people food—in training or just as a general reward—may give the dog the idea that such food is fair game. It might encourage your pet to steal food from the table or from people, especially kids or guests.
In addition, many human foods can be toxic to dogs. These include chocolate, grapes, raisins, macadamia nuts, and xylitol (a sweetener often used in gum, candy, and baked goods).
As an alternative to table scraps, you could train your dog with snacks that are tasty, low in fat, and commercially prepared for training. But keep in mind that soft chew snacks may be high in sugar, which is bad for dental health. When shopping for treats, read package labels and choose premium varieties that list meat as the first ingredient.
Use only small amounts for training purposes—treats should not interfere with the consistency of a normal diet or greatly affect the caloric intake for the size and age of the dog. The training sessions should be short in length and repeated several times throughout the day. For young dogs, the training period should be no longer than five minutes.
Finally, the most important training tip is to keep it positive. If you're getting frustrated with your puppy's naturally short attention span, take a break. Strive to end the session on a positive note so your pet will be eager for the next time.
Janet Tobiassen, DVM, a veterinarian based in the state of Washington, has been practicing and writing about vet medicine since 1999. She started training dogs at age 12, through 4-H, and continued pet therapy and obedience training in veterinary school and beyond.
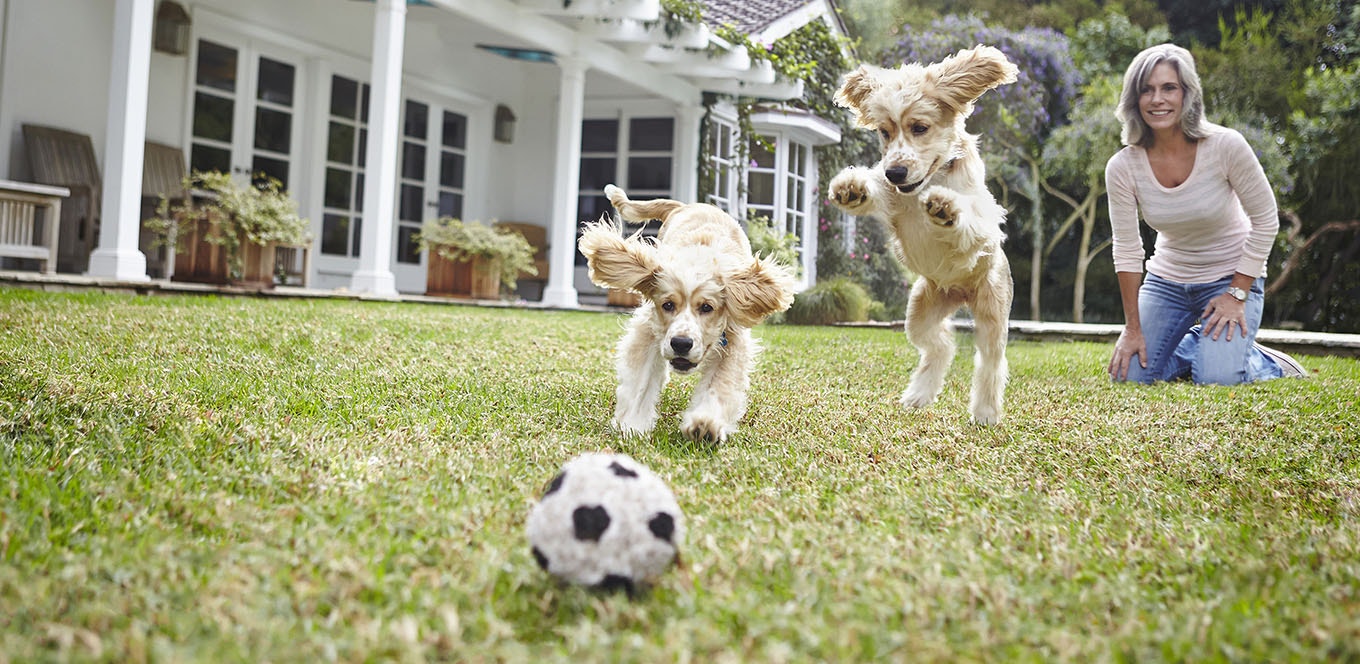



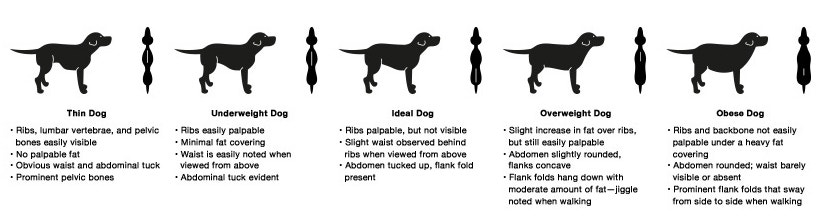
Assessing body condition is an important step in the overall evaluation of a companion animal's nutritional well-being.
Particularly in cases where the dog appears to be obese or underweight, it is important to evaluate total health of the dog before a proper nutritional management program is selected. The following body condition charts help explain body condition terms.