If you own a dog, chances are, you deal with the nuisance of shedding fur. Fortunately, there are some easy ways to help keep your dog's shedding to a manageable level.
If you own a dog, chances are, you deal with the nuisance of shedding fur. Fortunately, there are some easy ways to help keep your dog's shedding to a manageable level.
The main factor related to how much your dog sheds is which breed you own. Certain breeds, such as Yorkshire Terriers and Poodles, hardly shed at all, and are especially well suited for people who suffer from dander-related allergies. But if one of these hypoallergenic breeds is not your dog of choice, then chances are you deal with some amount of shedding. Here are some practical tips to deal with all of that hair.
Many dogs are seasonal shedders. As the temperatures begin to drop, so does the fur. Dogs shed their summer coats in the fall as their winter coats come in. The best way to deal with this is to be prepared. Brush your dog more often and vacuum more frequently. This will keep that extra hair from becoming too unmanageable.
Dogs also will go through their own version of spring cleaning. When the temperatures begin to rise in the spring, dogs will begin shedding that extra winter hair. Again, preparation is the key. Regular brushing and vacuuming will help you get through these “hairy” times.
Between the millions of strands of hair constantly growing, some breeds of dogs grow up to a total of 100 feet of fur per day! But, while your dog might not boast those kinds of hair-growth numbers, constantly replacing fur still places a demand on a dog’s system. Thirty percent of a dog's protein needs go toward hair growth. If a dog is not receiving proper nutrition, the dog's body will put the protein he's receiving toward maintaining muscle mass, leaving the coat to suffer.
A healthy, shiny coat is not only a sign of proper nutrition, but it also sheds less than an unhealthy coat. Premium dog food like IAMS™ ProActive Health™ provides dogs with the nutrients they need to keep their coat healthy, which means less shedding.
Brushing doesn't have to be a necessary evil. Train your dog to enjoy brushing, offering frequent praise during the process, and maybe even a treat at the end. This is easiest done from the time your dog is a puppy, but older dogs can be taught to enjoy brushing as well. The importance of brushing cannot be overemphasized. Just look at all the hair that ends up in the brush, and realize if it weren’t in the brush, it would be on your couch, floor, and perhaps, bed.
Be sure you're using the right kind of brush for your dog's coat. Breeds with thick undercoats need a specific type of brush, while longhaired breeds need a comb.
Last but not least, make sure to give your dog an occasional bath. Aside from the obvious benefit of having a clean, good-smelling pooch, your dog's coat will also benefit. Be warned though: Bathing your dog too frequently washes away the natural oil on his skin and coat, resulting in dry skin and, you guessed it, more shedding.
Committing the time to maintaining your dog's coat will help keep his shedding under control. Frequent brushing and vacuuming, and feeding your dog a balanced diet such as IAMS ProActive Health Adult MiniChunks will have you worrying less about an overabundance of hair and more time enjoying your furry friend.


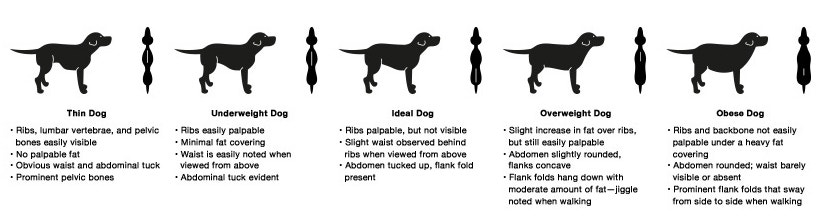
Assessing body condition is an important step in the overall evaluation of a companion animal's nutritional well-being.
Particularly in cases where the dog appears to be obese or underweight, it is important to evaluate total health of the dog before a proper nutritional management program is selected. The following body condition charts help explain body condition terms.