IAMS research has shown that some dog-food products are best formulated using a combination of carbohydrate sources. All IAMS dog foods are formulated precisely to meet the nutritional needs of your dog in his life stage. Such a combination offers optimal digestibility and helps maintain energy levels.
Our dog foods contain a variety of carbohydrate ingredients:
Barley: IAMS uses ground whole-grain barley that's cooked at high temperatures and finely ground in our dry dog-food formulas as part of our patented carbohydrate blend.
Corn: IAMS uses high-quality corn kernels that have been finely ground to break up the outside covering of each kernel, and then cooked at high temperatures to increase digestibility.
Grain sorghum: Also called milo, it is cracked, finely ground, and cooked before it is added to our dry dog foods. It is another carbohydrate source in our patented carbohydrate blend.
Rice flour: Our foods contain small kernels of white rice that have been separated from the larger kernels of milled rice, ground, and cooked at high temperatures to optimize digestibility.
Wheat: This is another high-quality carbohydrate source. In our biscuits, the wheat is an excellent, palatable carbohydrate source and adds a firm texture to the biscuit during the baking process.
Highly digestible diets are an important factor in the well-being of your dog. They deliver more essential nutrients more efficiently, so there is less waste.
Innovative and patented research by IAMS scientists has found that when the complex-carbohydrate sources grain sorghum and barley are used in a dog's diet, their breakdown is enhanced at another level.
These carbohydrate sources are all highly digestible, meaning your dog's body will still metabolize a high percentage of each for energy. What's unique about these grains is that they break down slowly and evenly, providing a stable source of energy.
The slow, even breakdown of grain sorghum, corn, and barley results in moderate, stable blood glucose levels after a meal. By minimizing swings in blood glucose, diets containing such a blend supply sustained energy. IAMS holds a patent on using grain sorghum and barley in a blend for dogs.


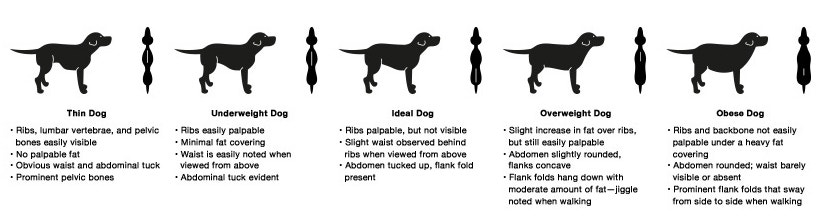
Assessing body condition is an important step in the overall evaluation of a companion animal's nutritional well-being.
Particularly in cases where the dog appears to be obese or underweight, it is important to evaluate total health of the dog before a proper nutritional management program is selected. The following body condition charts help explain body condition terms.