Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that isn't digested by a cat's gastrointestinal tract. It is important for cat health, because it provides bulk to move food through. Some types of fiber can be fermented (broken down by bacteria) in the system. This process creates short-chain fatty acids (SCFA), which are an important energy source for the cells lining the intestinal tract.
Today, people are more aware of fiber and its role in their diet. Studies showing the beneficial effects of higher fiber levels in humans influence the way many people think about their own food and that of their pets. Some manufacturers now apply the recommendations of human nutritionists and make high-fiber diets for cats, but cats have a much shorter digestive tract than we do. And unlike humans, cats are carnivorous, so their nutritional needs are better satisfied with meat rather than plant matter. Therefore, cats have different dietary needs than humans. For more than 60 years, companion animal nutritionists at IAMS™ have been studying diets to meet the special nutritional needs of cats.
IAMS Company research shows the optimal crude fiber level for healthy cats ranges from 1.4% to 3.5%. At these levels, nutrient breakdown is maximized. In unique situations, such as hairballs, higher fiber levels may be beneficial.
An important characteristic of fiber is its fermentability, or how well it can be broken down by bacteria in the intestine. This breakdown produces short-chain fatty acids, which provide energy to the intestines. Fiber varies in fermentability. Fiber sources used in pet foods include cellulose, which is poorly fermentable; beet pulp, which is moderately fermentable; and gums and pectin, which can be highly fermentable. Research has shown that moderate levels of moderately fermentable fiber, such as beet pulp, provide the benefits of energy for the intestinal lining and bulk, without the negative effects of excessive stool or gas and, therefore, are beneficial in cat diets.
High levels of poorly fermentable fiber are used in some weight-reduction pet foods to dilute the calories in a serving. IAMS Company research shows that high fiber levels can make it harder to digest other nutrients in the food and, in turn, reduce the nutritional quality of a cat's diet. Your cat making more trips to the litter box can be a result.
When choosing a pet food, fiber is an important consideration, but remember that the needs of cats are not the same as those of humans. A moderate level of moderately fermentable fiber, such as beet pulp, provides proven nutritional benefits for cats. Cat diets containing high levels of poorly fermentable fiber dilute calories and deprive cats of the nutrients they need.
All IAMS products are made with levels of moderately fermentable fiber needed to promote intestinal health. And all IAMS foods contain the moderately fermentable fiber system, which is the exclusive property of IAMS Company and is protected by U.S. Patent No. 5,616,569 for Pet Food Products Containing Fermentable Fibers and Process for Treating Gastrointestinal Disorders.
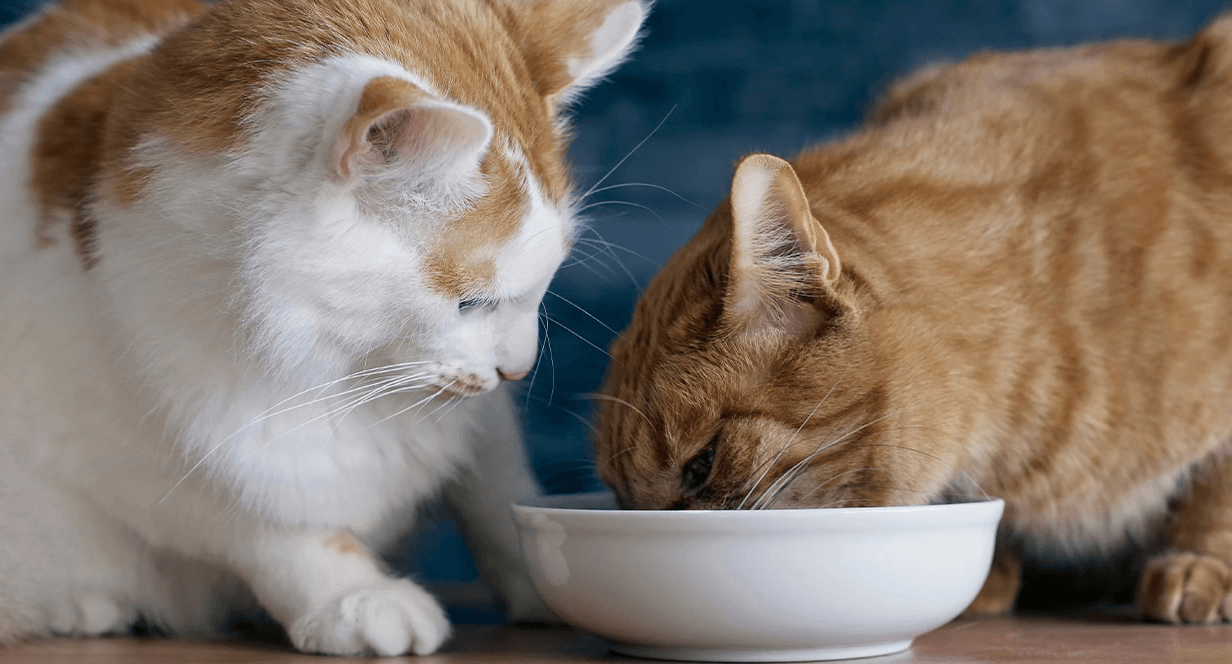


The only thing better than owning a cat is owning more than one cat. While a multiple-cat household means additional snuggles and cuddles, it can also mean a little extra work when it comes to mealtime. Fear not! We’ve assembled this tasty buffet of tips to help make sure all your feline companions get the proper amount of food and nutrition.
Similar to their humans, cats’ diets vary for a number of reasons.
Now, how can you make sure each cat is eating the right food come suppertime?
Make any changes to your cats’ diets gradually over the course of several days. This will help reduce stomach issues or requests to “speak with the manager.”
Instead of setting up a 24-hour buffet, schedule regular times for dining. This helps ensure your cats are hungry when it’s time to eat and won’t steal from anyone else’s dish throughout the day.
The best way to prevent fights over food or other eating issues is to keep an eye on your cats when you feed them. You’ll be certain everyone is getting a proper meal, and you’ll get some extra time to hang out together.
Try feeding each cat in a different room, putting their food bowls far apart or separating eating spaces with a barrier like a baby gate, trash can or chair.
Another option is to put one cat’s meal on the floor and the other’s on a countertop. This works well if one of your cats is older or heavier and can’t make the leap.
Your furry friends might not take to these changes immediately, but kind words, your ongoing affection and judicious use of treats will go a long way toward having them accept a new mealtime routine.